What is IoT? Internet of Things Explained with Examples
7 min read
Summary
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become one of the most critical technologies of the 21st century and an essential part of our lives, sometimes without us even realizing it. IoT refers to the interconnection of physical objects, embedding software, sensors, and other technologies, connected into a network (locally or to the Internet). This allows these objects to collect and exchange data.
The IoT has already begun to revolutionize our lives and lifestyles. It can make our homes more comfortable and energy efficient, help us navigate cities better, and improve our health and well-being. So, what are these possibilities, and what are the key components of IoT? Read on to find out.
What Is IoT
Kevin Ashton, a British technology pioneer, coined the term “the Internet of Things” in 1999. The IoT is a system of interconnected devices and objects – called “things” – that can collect and exchange data. Or, put even more simply, IoT means “taking all the things in the world and connecting them to the Internet.”
Making everyday objects more intelligent and connected makes our lives easier and more convenient. So much so that the number of IoT devices worldwide will nearly triple from 9.7 billion in 2020 to more than 29 billion in 2030. China is where the IoT will be used the most, with around 5 billion devices expected there.
How IoT works
IoT devices can range from simple sensors to more complex machines, such as vehicles, buildings, home appliances, and many others. When connected to a network and communicating, data is collected from these devices and transmitted wirelessly to a central location. The system can also use machine learning to improve its performance over time. IoT devices can connect and communicate whether they’re processing data in the cloud, over Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, or through various assistants made by Apple, Amazon, Google, and others.
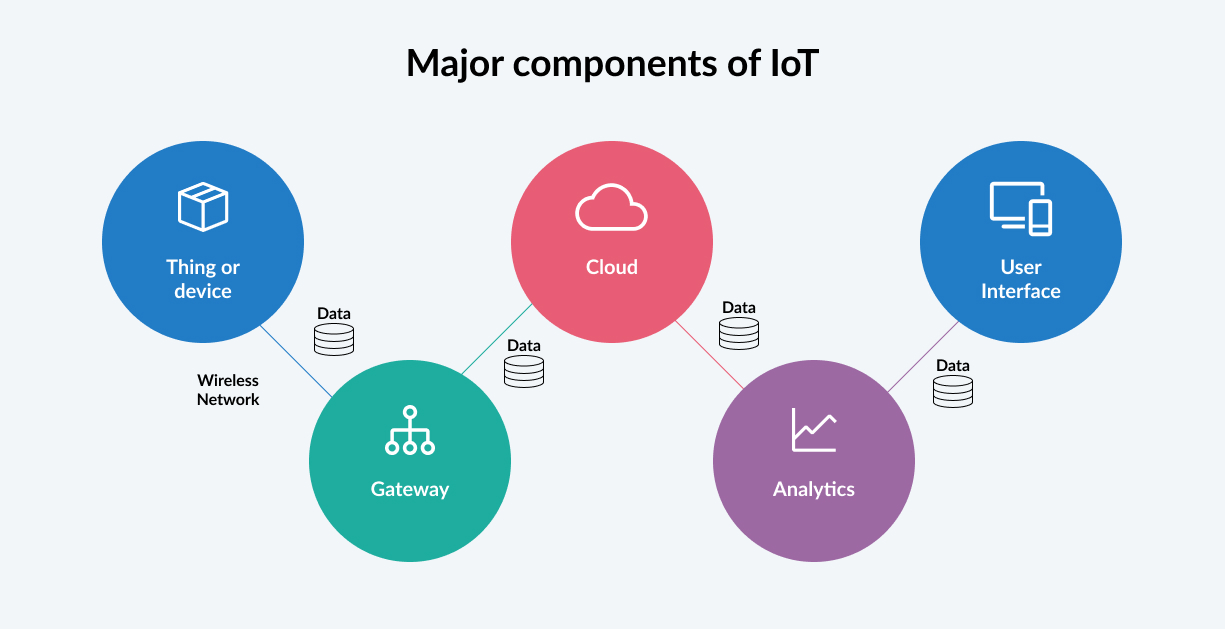
Types of IoT
With so many IoT devices, it’s necessary to narrow down IoT applications based on their uses. Some of the most common are:
Consumer IoT: Wearable IoT devices are becoming increasingly popular. They can record fitness data, monitor heart rate, and even provide real-time translations. In addition, home automation systems allow homeowners to remotely control their lighting, appliances, and security systems.
IoT in healthcare is used to collect patient data and improve the quality of care.
Industrial IoT is used to increase efficiency and safety in factories and other industrial areas.
Military IoT: Used primarily for applying IoT technologies in the military sector, like surveillance drones, robots, and biometrics for combat.
Transportation IoT: Includes things like connected cars and intelligent traffic management systems.
Consumer IoT applications
Home automation
Home automation integrates household appliances and systems to provide greater comfort, security, and energy efficiency. IoT plays an important role here by connecting devices and enabling them to share data and feedback. Connecting various devices and appliances to the Internet allows us to control them remotely and automate many tasks. This makes the devices more intelligent and responsive to their environment and users’ needs.
One of the most promising applications of IoT in home automation is its potential to help us save energy. Connecting devices and appliances to the Internet allows us to monitor their power consumption and adjust to reduce waste. For example, we can set timers on lights and appliances, so they automatically turn off when not in use. We can also receive alerts when an appliance is left on too long. A smart thermostat can learn your temperature preferences and adjust accordingly. Or, a security system that uses facial recognition can unlock your door when you come home.
The possibilities are endless when integrating IoT into home automation, with solutions that make our homes more comfortable, convenient, and secure. As smart homes get smarter every day, the future of IoT home automation is an exciting area to watch.
Connected cars
Connected cars are becoming increasingly common. As a result, various manufacturers offer vehicles with built-in connectivity features. Here’s a look at how the IoT is changing the car landscape: For starters, connected cars can communicate with each other and with infrastructures such as traffic lights and road signs. This makes for smoother traffic flow and can help prevent accidents. In addition, connected cars can be equipped with sensors that collect data on everything from tire pressure to fuel levels. This data can improve the car’s efficiency and make driving more enjoyable.
There are 5 ways a vehicle can be connected and communicate with its environment:
V2I “Vehicle to Infrastructure”: Technology captures vehicle-generated data and provides information about the infrastructure to the driver. V2I technology communicates information about safety, mobility, or environmental conditions.
V2V “Vehicle to Vehicle”: The technology communicates information about the speed and position of surrounding vehicles through wireless information exchange. The goal is to avoid accidents, alleviate traffic congestion and positively impact the environment.
V2C “Vehicle to Cloud”: The technology exchanges information about and for vehicle applications with a cloud system. This allows the vehicle to use data from other cloud-connected industries, such as energy, transportation, and smart homes, and leverage the IoT.
V2P “Vehicle to Pedestrian”: The technology takes information about the environment and communicates it with other vehicles, infrastructure, and personal mobile devices. This allows the car to communicate with pedestrians and is expected to improve road safety and mobility.
V2X “Vehicle to Everything”: This technology connects all types of vehicles and infrastructure systems, like cars, highways, ships, trains, and airplanes.
Smart cities
A smart city is an urban area where sensors and data analytics gather information about everything from traffic patterns to energy consumption. This data is then used to manage the city’s resources more efficiently and improve the quality of life for residents. Smart cities are constantly evolving and becoming more complex. And to keep up with the demand for data and services, cities are turning to the Internet of Things.
IoT in smart cities refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects connected to the Internet. These devices collect and share data about their environment and can be controlled remotely.
The IoT can help city managers make better infrastructure, resources, and services decisions. It can also save citizens time, money, and energy.
There are many potential applications for IoT in smart cities. For example, smart meters can help utilities manage demand and save customers money on energy bills. Traffic light systems can be connected using sensors to optimize traffic flow. This saves time and fuel and reduces emissions from idling vehicles. Trash cans can be equipped with sensors that send alerts when they need to be emptied, saving labor costs and making the streets cleaner.
With the advent of the IoT, smart cities are becoming a reality, and in the future, IoT will play an even more prominent role. It will help city managers make real-time decisions based on data from multiple sources and, ultimately, give residents more control over their environment.
Enterprise IoT applications
Retail
IoT in retail brings salespeople closer to their customers than ever before, bringing value to both sides of the receipt.
Retailers can now use connected devices to monitor customer activity in their stores. Real-time data on customer buying habits, preferences, and feedback enable many customizations. Among the most important are inventory management, pricing strategies, and adjusting promotions based on what customers are most likely to buy or respond positively to.
Retailers can also use digital signage screens with location-based content tailored specifically to a person’s current position in the store. This can increase sales and make it easier for customers to find what they need quickly and efficiently. With Smart Shelves, IoT-enabled weight sensors, cameras, and other accessories monitor real-time store performance. This data helps them promptly identify areas needing attention, improvements, or restocking.
Logistics
IoT is revolutionizing the way we think about logistics by changing how goods are moved and tracked, making the process easier and more reliable than ever.
Companies can also use IoT in logistics to improve efficiency and track shipments. For example, IoT devices such as sensors and RFID tags can be attached to shipments to track their location and monitor their condition in real time. This allows logistics companies to quickly identify and fix problems that occur during transportation, such as delays or damage.
It can also be used to optimize routes and schedules to reduce the time and cost of delivering goods. Overall, the use of IoT in logistics has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of the supply chain.
The road ahead for companies
Aside from being required to process increasingly large amounts of data from the IoT, companies are becoming more aware of the value of sustainability and social responsibility in their operations. However, they are under pressure from regulators, investors, and customers to demonstrate improvements in these areas. To meet these expectations, companies must find ways to verify and demonstrate their sustainability efforts. One tool that can help companies organize and systematize data and do it in a sustainable and socially responsible way is IBM Envizi’s ESG Suite.
The importance and challenges of building a sustainable business and managing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) indicators are more significant than ever. IBM Envizi’s ESG Suite platform helps automate the collection and consolidation of over 500 data types and supports key ESG reporting frameworks. With customizable dashboards and visualizations, the platform enables organizations to manage environmental goals, identify efficiency opportunities, and assess sustainability risks.
Benefits
Helps build a data foundation
Enables a single system of record that delivers auditable, finance-grade ESG and sustainability data
Streamlines reporting
Provides flexible reporting tools to meet internal and external ESG and sustainability reporting requirements
Helps engage stakeholders
Integrates internal and external stakeholders, process and technology to embed sustainability into daily operations
Helps accelerate decarbonization
Unlocks insights to inform the fastest and most cost-effective pathway to decarbonization
Learn more about IBM Envizi ESG Suite platform.
Conclusion
It’s undeniable that the IoT has such an impact that it’s impossible to imagine our future without it. The IoT is a powerful tool that can simplify our lives and has already begun to revolutionize the way we live, play, and work.
However, we must be careful not to over-rely on the IoT. We also need to be aware of the potential security risks and take steps to protect our devices and data. As with any new technology, some challenges must be overcome before it can reach its full potential. However, with the right approach and these precautions, these challenges can be overcome, and the IoT can become a transformative force for good.
At InnoBoost, we can help you join this constantly-growing world of IoT. Integrating IoT into your current operations, automating and securing your processes, and improving your data collection are just some of the things we can do together today to set your organization up for success tomorrow.
Contact us to schedule a meeting and find out more about how IoT can help your business.
1https://www.iotforall.com/what-is-internet-of-things
2https://www.statista.com/statistics/1183457/iot-connected-devices-worldwide/
3http://autocaat.org/Technologies/Automated_and_Connected_Vehicles/
4 https://www.its.dot.gov/v2i/
5https://www.nhtsa.gov/technology-innovation/vehicle-vehicle-communication
6https://www.abiresearch.com/market-research/product/1022093-connected-vehicle-cloud-platforms/
7https://www.its.dot.gov/research_archives/safety/v2p_comm_safety.htm
You may also like…
Unlocking the Power of Custom AI with InstructLab
5 min readSummary In the dynamic landscape of artificial intelligence, the ability to create models tailored to unique business needs is more than a competitive edge—it's a necessity. InstructLab, a collaborative initiative from IBM and Red Hat, is revolutionizing AI...
Strengthening Authentication in the Digital Age with IBM Verify
5 min readSummary In today’s interconnected world, the importance of robust authentication systems cannot be overstated. As digitalization accelerates, safeguarding sensitive data and critical systems has become a top priority for businesses. Effective access...
From Data Chaos to Data Confidence: Real-World Use Cases of IBM Data Product Hub
5 min readSummary In a world where data streams in from every direction—transactions, patient records, supply chain logs, and more—businesses often face “data chaos.” Instead of powering innovation, their data sits scattered in different formats and systems, making it...
Headquarters
InnoBoost SA
Route de Genolier 18
1271 Givrins
Office
InnoBoost SA
EPFL Innovation Park
Building E, Module 007
1015 Lausanne
© 2016-2022, InnoBoost SA. All rights reserved – Usage conditions – Graphic design by Emblematik Sàrl